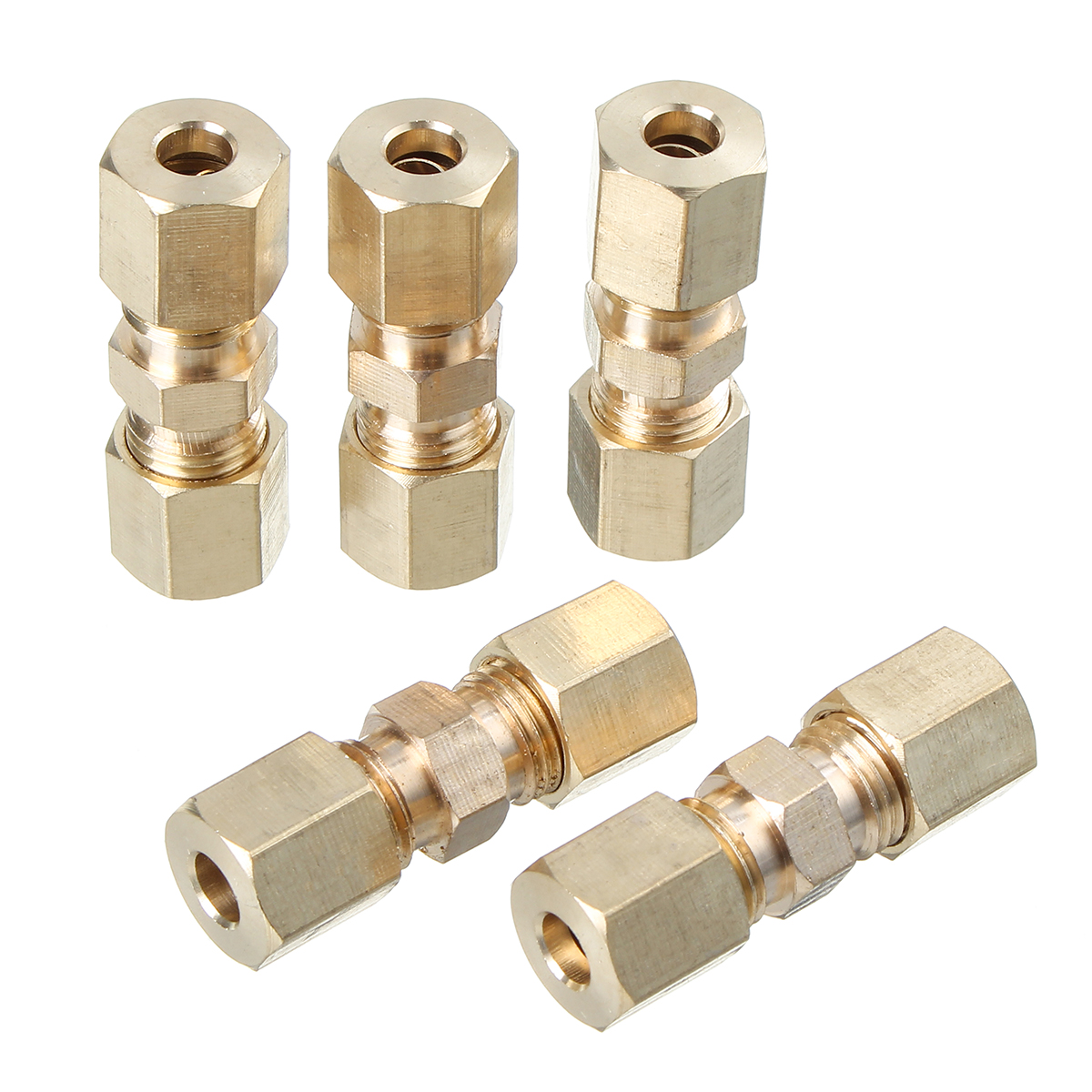
3 16 compression fitting for brake line – Delve into the world of brake line fittings with our comprehensive guide to 3/16 compression fittings. This essential component ensures a secure and leak-free connection, safeguarding your braking system’s integrity. Join us as we explore the intricacies of installation, compatibility, and troubleshooting, empowering you with the knowledge to tackle any brake line challenge with confidence.
Brake Line Compatibility
3/16 compression fittings are specifically designed to work with brake lines, providing a secure and leak-free connection. Brake lines come in various types, each with its unique characteristics and compatibility with compression fittings.
Types of Brake Lines
- Steel Brake Lines:These lines are highly durable and resistant to corrosion, making them a popular choice for heavy-duty applications. 3/16 compression fittings are commonly used with steel brake lines, ensuring a tight and reliable connection.
- Stainless Steel Brake Lines:Known for their exceptional corrosion resistance, stainless steel brake lines offer increased durability compared to steel lines. They are also compatible with 3/16 compression fittings, providing a long-lasting and leak-free connection.
- Copper-Nickel Brake Lines:These lines are highly flexible and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for tight spaces and custom installations. 3/16 compression fittings can be used with copper-nickel brake lines, ensuring a secure and flexible connection.
- Nylon Brake Lines:Nylon lines are lightweight and flexible, making them easy to install. They are not as durable as metal lines but are commonly used in low-pressure brake systems. 3/16 compression fittings are not typically used with nylon brake lines due to their different material properties.
It is crucial to use the correct compression fitting for the specific brake line to ensure a proper seal and prevent leaks. The type of brake line, its material, and diameter should be considered when selecting the appropriate compression fitting.
Installation Procedures
Installing a 3/16 compression fitting on a brake line is a straightforward process that requires minimal tools and expertise. By following these step-by-step instructions and incorporating the tips and techniques provided, you can ensure a secure and leak-free installation.
Tools Required
- 3/16 compression fitting
- Brake line cutter
- Deburring tool
- Wrench
Step-by-Step Instructions, 3 16 compression fitting for brake line
- Cut the brake line:Use a brake line cutter to make a clean, perpendicular cut on the brake line where the fitting will be installed.
- Deburr the cut end:Remove any burrs or sharp edges from the cut end of the brake line using a deburring tool.
- Insert the brake line into the fitting:Insert the cut end of the brake line into the compression fitting until it reaches the stop.
- Tighten the compression nut:Using a wrench, tighten the compression nut onto the fitting body. Apply sufficient torque to compress the ferrule onto the brake line, but avoid overtightening.
- Inspect for leaks:Once the fitting is installed, inspect the connection for any leaks. Apply pressure to the brake line and check for any fluid seepage.
Tips and Techniques
- Use a sharp brake line cutter to ensure a clean cut.
- Deburr the cut end thoroughly to prevent leaks.
- Tighten the compression nut securely, but avoid overtightening, which can damage the fitting.
- Inspect the connection for leaks both before and after applying pressure to the brake line.
- If you encounter any leaks, disassemble the fitting, inspect the components for damage, and reassemble the fitting.
Materials and Tools
Installing a 3/16 compression fitting requires the right materials and tools to ensure a secure and leak-free connection. Using high-quality components and proper tools is crucial for a successful installation.
The following are the essential materials and tools you’ll need:
Materials
- 3/16 compression fitting:Choose a fitting that is compatible with the brake line material and size.
- Brake line:Use a high-quality brake line that is compatible with the fitting and the brake system.
- Compression sleeve:The sleeve helps create a seal between the fitting and the brake line.
Tools
- Tube cutter:Use a sharp tube cutter to ensure a clean and perpendicular cut on the brake line.
- Compression fitting tool:This specialized tool is designed to properly tighten the compression fitting.
- Wrench:A wrench is needed to tighten the fitting onto the brake line.
Troubleshooting Common Issues: 3 16 Compression Fitting For Brake Line
The installation and use of a 3/16 compression fitting typically goes smoothly, but occasional issues can arise. Identifying and resolving these problems promptly ensures a secure and reliable connection.
Proper maintenance and regular inspection are crucial for preventing problems and ensuring the fitting’s longevity. Addressing any issues promptly helps maintain optimal performance and extends the fitting’s lifespan.
Leakage
Leakage is a common issue that can occur due to various reasons. The most common cause is an improper seal between the fitting and the tubing. Ensure the ferrule is properly tightened and the tubing is inserted fully into the fitting.
For a hassle-free way to connect your brake controller to your vehicle’s wiring harness, consider the Universal Pig-Tail Brake Controller Wiring Harness . This harness features a universal design that makes it compatible with most brake controllers and vehicles, eliminating the need for splicing or cutting wires.
Its durable construction and weather-resistant connectors ensure long-lasting performance, making it an excellent investment for your towing setup.
If leakage persists, check for any damage to the fitting or tubing and replace if necessary.
Loose Connection
A loose connection can compromise the fitting’s integrity and lead to leaks or other problems. Tighten the fitting securely, but avoid overtightening as this can damage the fitting or tubing. If the connection remains loose, inspect the threads for any damage or wear and replace the fitting if necessary.
Corrosion
Corrosion can occur over time, especially in environments with moisture or corrosive elements. Regular inspection and maintenance are essential for preventing corrosion. Clean the fitting periodically and apply a corrosion-resistant lubricant to protect it from the elements.
Clogged Fitting
Debris or dirt can accumulate in the fitting over time, causing it to become clogged. This can restrict the flow of fluid and lead to performance issues. Regularly clean the fitting and remove any debris to ensure proper operation.
Safety Precautions

Prioritizing safety is paramount when handling brake lines and compression fittings. Improper installation or mishandling can lead to severe consequences, including accidents and injuries. Therefore, it is imperative to adhere to specific safety guidelines to ensure a safe and successful installation and maintenance process.
Before commencing any work, it is crucial to don appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and closed-toe shoes. These measures safeguard you from potential hazards like brake fluid splashes or flying debris.
Potential Risks and Hazards
- Brake Fluid Leakage:Improperly installed compression fittings can lead to brake fluid leakage, compromising the braking system’s integrity and potentially causing accidents.
- System Failure:If the brake lines are not properly connected or sealed, the entire braking system may fail, leading to a complete loss of braking ability.
- Personal Injury:Mishandling brake lines or compression fittings can result in cuts, abrasions, or even more severe injuries due to the presence of sharp edges or pressurized brake fluid.
Comparison with Other Fittings
Compression fittings are commonly used in brake line applications due to their ease of installation and reliability. However, there are other types of fittings available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Flared Fittings
Flared fittings require specialized tools and expertise to install. They provide a strong and leak-proof connection, but can be time-consuming to assemble.
Inverted Flare Fittings
Inverted flare fittings offer a tighter seal than flared fittings, but they are even more difficult to install. They are typically used in high-performance applications where a secure connection is critical.
Compression Fittings vs. Other Fittings
The following table summarizes the key differences between compression fittings and other types of brake line fittings:| Fitting Type | Ease of Installation | Leak Resistance | Strength | Cost ||—|—|—|—|—|| Compression | Easy | Good | Moderate | Moderate || Flared | Difficult | Excellent | Excellent | High || Inverted Flare | Very Difficult | Excellent | Excellent | Very High |
Whether you’re a seasoned truck inspector or a weekend warrior, the Brake Tech Tools Original Truck Inspector is an essential tool for any vehicle inspection. Its rugged construction and easy-to-use design make it perfect for checking brake pads, rotors, and calipers, while the included carrying case ensures that you can take it with you wherever you go.
With its affordable price point, the Truck Inspector is a must-have for any serious truck owner or inspector.
Applications and Uses
3/16 compression fittings are extensively used in brake systems for various applications. They are commonly found in:
Vehicles
- Passenger cars
- Light trucks
- SUVs
- Motorcycles
Brake Systems
- Hydraulic brake lines
- ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) lines
- Brake caliper connections
- Master cylinder connections
Compatibility
Compression fittings are suitable for use with a variety of brake line materials, including:
- Steel
- Stainless steel
- Copper
- Nickel-plated copper
They are particularly well-suited for flexible brake lines, as they allow for easy adjustments and bending without compromising the integrity of the line.
Final Summary
Mastering the installation and maintenance of 3/16 compression fittings empowers you to maintain a reliable and responsive braking system. Remember, safety should always be your top priority when working with brake lines. By following our expert guidance, you can ensure your vehicle’s braking performance remains at its peak, providing peace of mind on every journey.
Questions and Answers
What types of brake lines are compatible with 3/16 compression fittings?
3/16 compression fittings are primarily compatible with steel brake lines, which are commonly used in older vehicles and certain heavy-duty applications.
What tools are essential for installing a 3/16 compression fitting?
You will need a flare nut wrench, a tubing cutter, a deburring tool, and a torque wrench to ensure a secure and leak-proof installation.
How can I troubleshoot a leaking 3/16 compression fitting?
Check for proper tightening, inspect the O-rings for damage, and ensure the brake line is correctly flared. If the issue persists, consult a qualified mechanic.