Transmission speed sensor location is a crucial aspect of maintaining optimal vehicle performance. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of TSSs, providing a thorough understanding of their purpose, placement, and troubleshooting techniques. Get ready to shift gears and embark on a journey to master the art of TSS management.
Transmission Speed Sensor (TSS) Overview
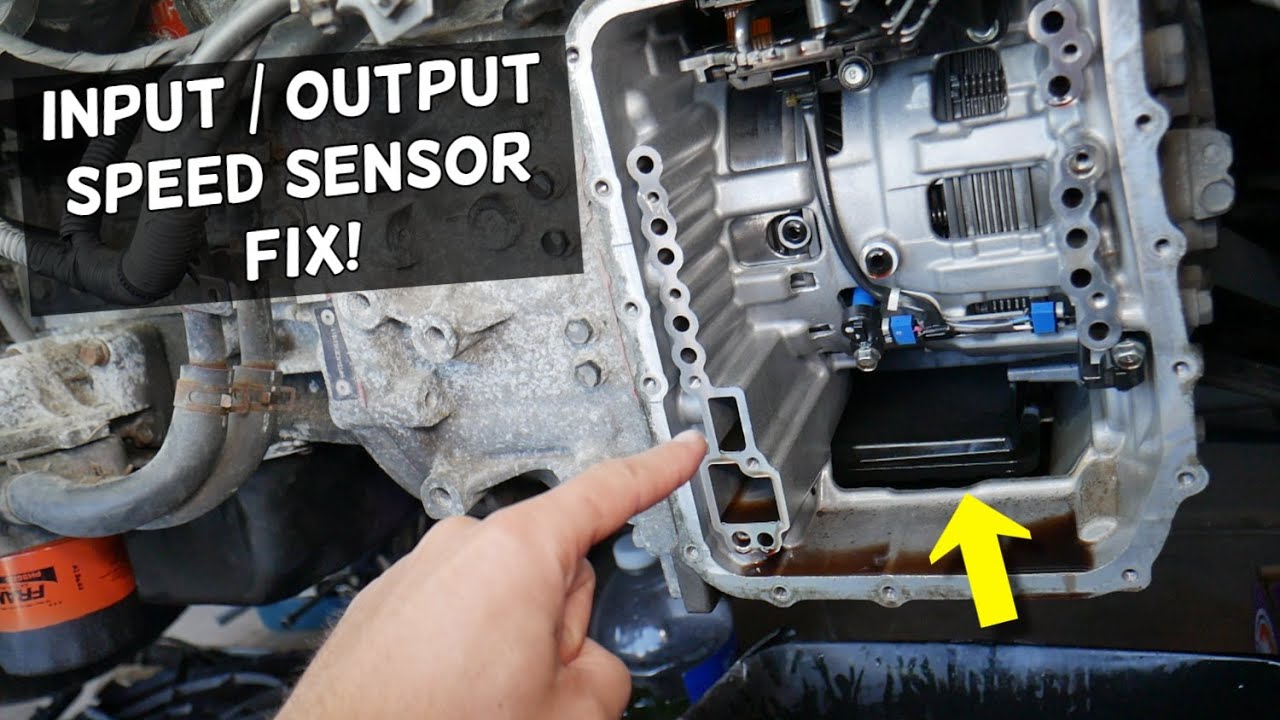
A transmission speed sensor (TSS) is a critical component in modern vehicles that monitors the rotational speed of the transmission output shaft. It plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient transmission operation, as well as enhancing vehicle safety and performance.
There are various types of transmission speed sensors, each designed for specific applications and vehicle models. Common types include magnetic, Hall effect, and optical sensors. Magnetic sensors use a permanent magnet to generate a magnetic field, while Hall effect sensors utilize the Hall effect to detect changes in magnetic fields.
Optical sensors employ a light source and a photodetector to measure the speed of the transmission output shaft.
The operating principles behind TSSs vary depending on the sensor type. Magnetic sensors generate a voltage proportional to the rotational speed, while Hall effect sensors produce a digital signal indicating the speed. Optical sensors measure the time it takes for a light beam to travel between the light source and the photodetector, which is inversely proportional to the rotational speed.
TSS Location and Identification
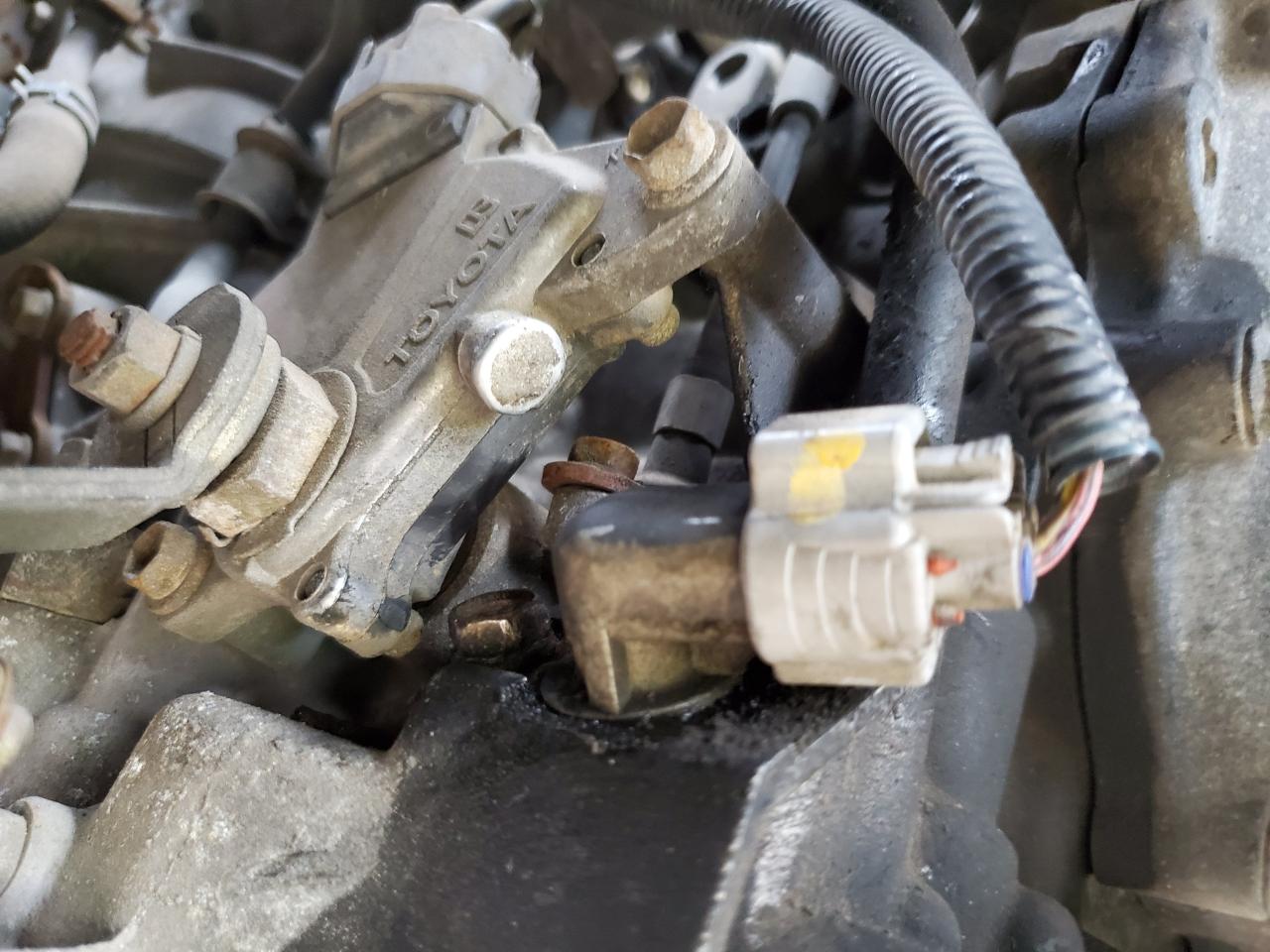

Transmission Speed Sensors (TSSs) are typically located on or near the transmission case, where they can monitor the speed of the transmission output shaft. The exact location of the TSS may vary depending on the vehicle model, transmission type, and design.
Factors Influencing TSS Placement
Several factors can influence the placement of TSSs, including:
- Transmission Type:The type of transmission (manual, automatic, continuously variable, etc.) can affect the location of the TSS.
- Transmission Design:The specific design of the transmission, such as the number of gears and the arrangement of the shafts, can also influence the placement of the TSS.
- Vehicle Model:Different vehicle models may have different transmission designs, which can lead to variations in TSS placement.
Identifying TSSs, Transmission speed sensor location
TSSs can usually be identified by their appearance and markings. They are typically small, cylindrical devices with a connector on one end. The TSS may have a label or marking that indicates its function, such as “Transmission Speed Sensor” or “TSS.”
TSS Installation and Removal
Installing and removing a Transmission Speed Sensor (TSS) requires careful handling and attention to safety protocols. Proper installation ensures accurate speed readings, while proper removal prevents damage to the sensor and surrounding components.
Installation
- Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake.
- Locate the TSS on the transmission housing. It is typically a cylindrical device with an electrical connector.
- Clean the mounting surface on the transmission housing.
- Apply a thin layer of sealant to the TSS mounting surface.
- Position the TSS in place and tighten the mounting bolts to the specified torque.
- Connect the electrical connector to the TSS.
Removal
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the TSS.
- Remove the mounting bolts holding the TSS in place.
- Carefully remove the TSS from the transmission housing.
- Clean the mounting surface on the transmission housing and the TSS.
- Inspect the TSS for any damage or wear before reinstallation.
TSS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics: Transmission Speed Sensor Location

Troubleshooting and diagnosing Transmission Speed Sensors (TSSs) involves identifying common issues and their symptoms, employing diagnostic procedures to pinpoint faulty TSSs, and implementing effective solutions to resolve related problems.
Common TSS Issues and Symptoms
- Inaccurate Speed Readings:Faulty TSSs can provide inaccurate speed readings, leading to incorrect transmission shift points and potential drivability issues.
- Transmission Slipping:A malfunctioning TSS can cause the transmission to slip, resulting in a loss of power and acceleration.
- Check Engine Light:TSS failures can trigger the Check Engine Light to illuminate, indicating a potential problem with the sensor or its circuit.
- Transmission Overheating:Faulty TSSs can contribute to transmission overheating by providing incorrect speed information to the transmission control module.
- Harsh Shifting:A TSS malfunction can cause harsh or delayed shifting, affecting the overall driving experience.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing TSS faults involves using diagnostic tools and procedures to identify the root cause of the problem. Common diagnostic techniques include:
- Visual Inspection:Inspecting the TSS for physical damage, corrosion, or loose connections can help identify potential issues.
- Electrical Testing:Using a multimeter to test the TSS’s electrical resistance, voltage, and continuity can help determine if the sensor is functioning properly.
- Scan Tool Diagnostics:Utilizing a scan tool can retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the TSS, providing valuable information about the sensor’s status.
- Oscilloscope Analysis:An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the TSS’s output signal, helping identify waveform abnormalities or signal dropouts.
Troubleshooting Tips and Solutions
- Clean Electrical Connections:Cleaning the electrical connections of the TSS and its wiring harness can resolve intermittent issues caused by corrosion or poor contact.
- Inspect Wiring:Check the wiring harness for any damage, breaks, or loose connections that may affect the TSS’s signal.
- Replace Faulty TSS:If the TSS is confirmed to be faulty through diagnostic testing, replacing it with a new sensor is necessary.
- Reset Transmission Control Module:In some cases, resetting the transmission control module (TCM) can resolve TSS-related issues by clearing any stored fault codes.
TSS Data Interpretation
Transmission Speed Sensors (TSSs) play a vital role in monitoring the transmission system’s performance and providing valuable data for diagnostics and maintenance. These sensors generate electrical signals that represent the rotational speed of the transmission’s input and output shafts, enabling the interpretation of crucial information about the transmission’s operation.
Analyzing TSS data involves understanding the significance of the generated signals and their implications for vehicle maintenance. The data helps assess the transmission’s performance, identify potential issues, and predict maintenance needs.
Signal Analysis
- Input Shaft Speed:Indicates the rotational speed of the transmission’s input shaft, which is connected to the engine’s crankshaft. This data provides insights into engine performance and the transmission’s ability to handle torque transfer.
- Output Shaft Speed:Represents the rotational speed of the transmission’s output shaft, which is connected to the driveshaft. Analyzing this data helps assess the transmission’s gear ratios, slippage, and overall efficiency.
- Ratio Calculations:By comparing the input and output shaft speeds, the transmission’s gear ratio can be calculated. This ratio indicates the relationship between the engine’s speed and the vehicle’s speed, providing information about the transmission’s performance under different driving conditions.
- Slippage Detection:TSS data can be used to detect transmission slippage, which occurs when the input and output shaft speeds differ significantly. Slippage can indicate worn or damaged transmission components, requiring prompt attention to prevent further issues.
Implications for Vehicle Maintenance
Interpreting TSS data has significant implications for vehicle maintenance and performance optimization. By monitoring and analyzing TSS signals, technicians can:
- Identify Transmission Issues:TSS data can reveal potential transmission problems, such as slipping clutches, worn gears, or faulty solenoids, enabling early detection and repair.
- Optimize Transmission Performance:TSS data can guide transmission tuning and adjustments to enhance performance, reduce fuel consumption, and improve overall driving experience.
- Predict Maintenance Needs:Analyzing TSS data over time can help predict maintenance requirements, such as fluid changes, filter replacements, or major overhauls, allowing for proactive scheduling and cost savings.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, transmission speed sensor location plays a pivotal role in ensuring smooth and efficient vehicle operation. By understanding the concepts Artikeld in this guide, you can effectively locate, troubleshoot, and maintain your TSS, maximizing its functionality and ensuring a seamless driving experience.
FAQ Section
Where are transmission speed sensors typically located?
TSS locations vary depending on the vehicle model and transmission type. Common locations include the transmission case, input shaft, or output shaft.
What are the symptoms of a faulty transmission speed sensor?
Faulty TSSs can cause various issues, such as incorrect speedometer readings, transmission slipping, or even engine stalling.
How do I troubleshoot a transmission speed sensor?
Troubleshooting involves checking for electrical continuity, signal strength, and comparing sensor readings with expected values.




