Coolant temp sensor location – Delve into the world of coolant temperature sensor locations, where precision meets performance. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of these crucial sensors, uncovering their impact on engine health and overall vehicle efficiency.
From various makes and models to sensor types and specifications, this guide will empower you with a comprehensive understanding of coolant temp sensor locations. Prepare to navigate the complexities of sensor installation, wiring, troubleshooting, and maintenance with ease.
Coolant Temperature Sensor Location
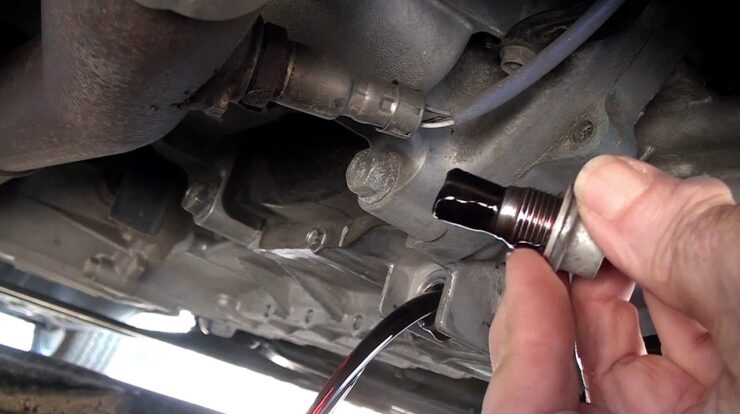
Locating the coolant temperature sensor in a vehicle is crucial for ensuring accurate temperature readings and optimal engine performance. The sensor’s position plays a vital role in its ability to effectively monitor coolant temperature and provide reliable data to the engine control unit (ECU).
Common Locations of Coolant Temperature Sensors
- Engine Coolant Outlet:Many vehicles have the coolant temperature sensor installed at the engine coolant outlet, where the coolant exits the engine block. This location provides a direct measurement of the coolant temperature as it leaves the engine, giving a good indication of the engine’s operating temperature.
- Radiator Inlet:Some vehicles have the sensor placed at the radiator inlet, where the coolant enters the radiator to be cooled. This location allows the sensor to monitor the temperature of the coolant before it enters the radiator, providing information about the effectiveness of the cooling system.
- Cylinder Head:In some cases, the coolant temperature sensor is installed directly into the cylinder head, close to the combustion chamber. This location provides a more accurate reading of the coolant temperature near the engine’s hottest areas, giving a good indication of the engine’s thermal load.
- Thermostat Housing:The coolant temperature sensor may also be located in the thermostat housing, which controls the flow of coolant through the engine. This location allows the sensor to monitor the coolant temperature as it passes through the thermostat, providing information about the engine’s operating temperature and the thermostat’s operation.
Sensor Types and Specifications
Coolant temperature sensors are crucial components in engine management systems, providing accurate temperature readings of the engine coolant. These sensors come in various types, each with unique operating principles, accuracy levels, and response times.
Thermistors
- Thermistors are semiconductor devices that exhibit a change in electrical resistance with temperature.
- They are typically made of metal oxides and have a negative temperature coefficient (NTC), meaning their resistance decreases as temperature increases.
- Thermistors are known for their high accuracy and fast response time, making them suitable for precise temperature monitoring.
Thermocouples, Coolant temp sensor location
- Thermocouples consist of two dissimilar metal wires joined at one end, creating a junction.
- When a temperature difference exists between the junction and the other ends of the wires, a voltage is generated at the junction, proportional to the temperature difference.
- Thermocouples offer a wide temperature range and are often used in harsh environments due to their durability.
Specifications
Common coolant temperature sensors have specific specifications that determine their performance:
- Temperature Range:The temperature range over which the sensor operates accurately.
- Resistance Values:The resistance values of thermistors at different temperatures.
- Signal Output:The electrical signal (voltage or current) generated by the sensor in response to temperature changes.
Installation and Wiring
Installing and wiring a coolant temperature sensor involves several crucial steps to ensure accurate temperature readings and proper engine operation. Here’s a detailed guide:
Installation
- Locate the designated mounting point for the coolant temperature sensor on the engine. This is typically near the thermostat housing or cylinder head.
- Clean the mounting surface thoroughly to remove any dirt or debris.
- Apply a small amount of thread sealant to the sensor’s threads.
- Carefully screw the sensor into the mounting point by hand, avoiding overtightening.
- Tighten the sensor using a torque wrench to the specified torque value.
Wiring
- Identify the wiring harness connector for the coolant temperature sensor.
- Connect the sensor’s electrical terminals to the corresponding terminals on the harness connector. Ensure the connections are secure and free of corrosion.
- Secure the wiring harness to prevent it from coming loose.
- Test the sensor’s operation using a multimeter or diagnostic tool to verify its accuracy.
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Identifying and resolving issues with coolant temperature sensors is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance. Common symptoms of a faulty sensor include inaccurate temperature readings, engine overheating, and poor fuel efficiency.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Procedures
- Check for Error Codes:Scan the vehicle’s computer for any stored error codes related to the coolant temperature sensor.
- Inspect Wiring and Connections:Visually inspect the sensor’s wiring and connectors for any damage or corrosion. Loose or damaged connections can affect sensor readings.
- Test Sensor Resistance:Using a multimeter, measure the sensor’s resistance at different temperatures. Compare the readings with the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the sensor is within the acceptable range.
- Simulate Temperature Changes:Submerge the sensor in a temperature-controlled bath and gradually increase the temperature while monitoring the sensor’s output signal. This helps verify the sensor’s response to temperature changes.
- Replace Sensor:If the troubleshooting procedures indicate a faulty sensor, replace it with a new one. Ensure the new sensor is compatible with the vehicle and properly installed.
Use of Diagnostic Tools and Equipment
Specialized diagnostic tools and equipment can aid in troubleshooting coolant temperature sensors. These tools may include:
- OBD-II Scanners:Used to retrieve error codes and monitor sensor readings in real-time.
- Multimeters:Measure voltage, current, and resistance, including the sensor’s output signal.
- Temperature-Controlled Baths:Simulate different temperatures to test the sensor’s response.
Maintenance and Replacement
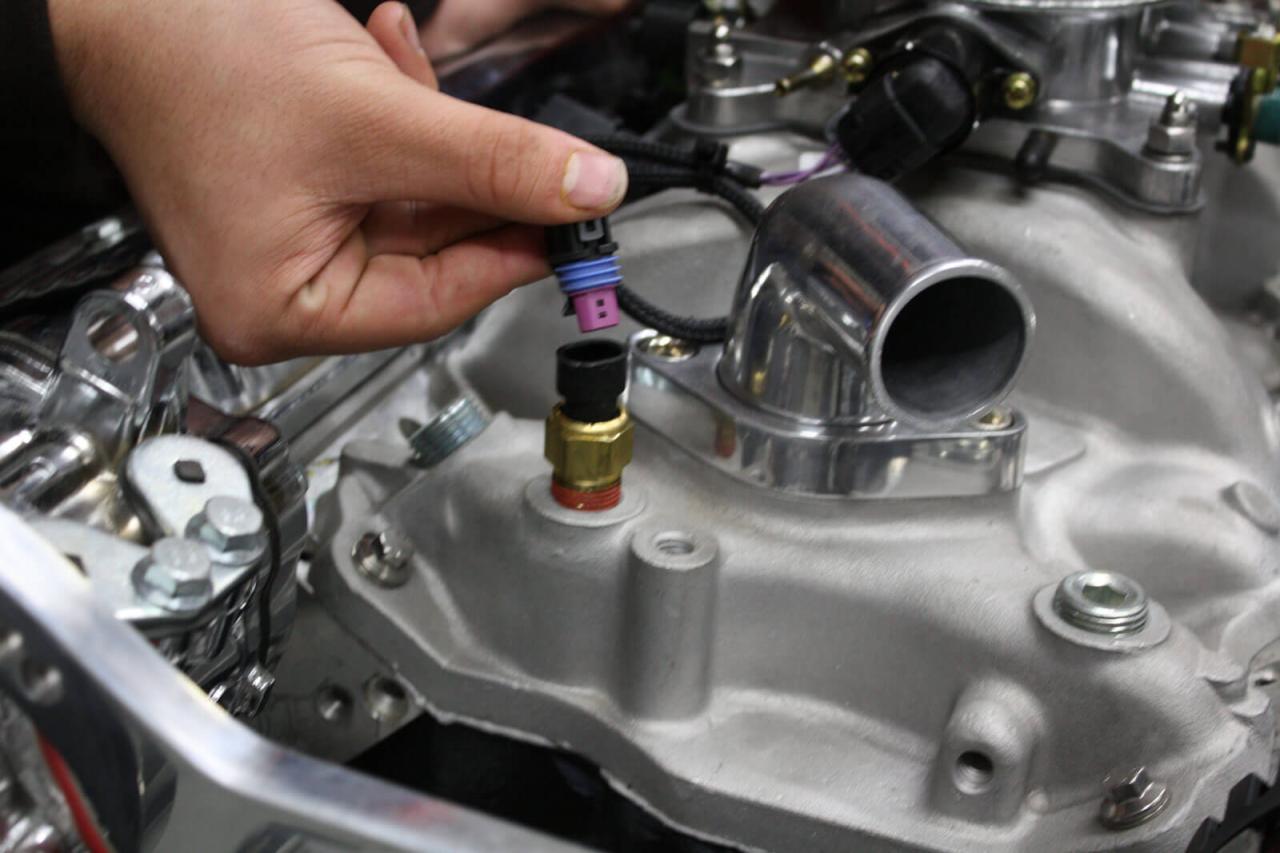

The coolant temperature sensor is a crucial component that requires regular maintenance and inspection to ensure optimal engine performance.
Inspection and Cleaning
Regularly inspecting the coolant temperature sensor is essential to prevent potential issues. Check the sensor for any signs of corrosion, damage, or loose connections. Clean the sensor using a non-abrasive cleaner and a soft brush to remove any dirt or debris that may interfere with its operation.
Replacement
If the coolant temperature sensor fails or becomes faulty, it’s imperative to replace it promptly. Ignoring sensor issues can lead to incorrect engine temperature readings, resulting in poor engine performance, increased emissions, and potential damage to the engine. It’s recommended to consult a qualified mechanic or refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the specific replacement procedure.
Last Recap: Coolant Temp Sensor Location
As we conclude our exploration of coolant temp sensor locations, remember that these humble components play a pivotal role in ensuring optimal engine operation. By embracing the knowledge gained from this guide, you can proactively maintain your vehicle, preventing costly repairs and maximizing its lifespan.
Answers to Common Questions
Where are coolant temperature sensors typically located?
Common locations include the engine block, cylinder head, radiator hose, and thermostat housing.
What factors influence coolant temperature sensor placement?
Factors include proximity to coolant flow, response time requirements, and ease of accessibility.
How often should coolant temperature sensors be inspected?
Regular inspections are recommended as part of routine vehicle maintenance, typically every 12-18 months.