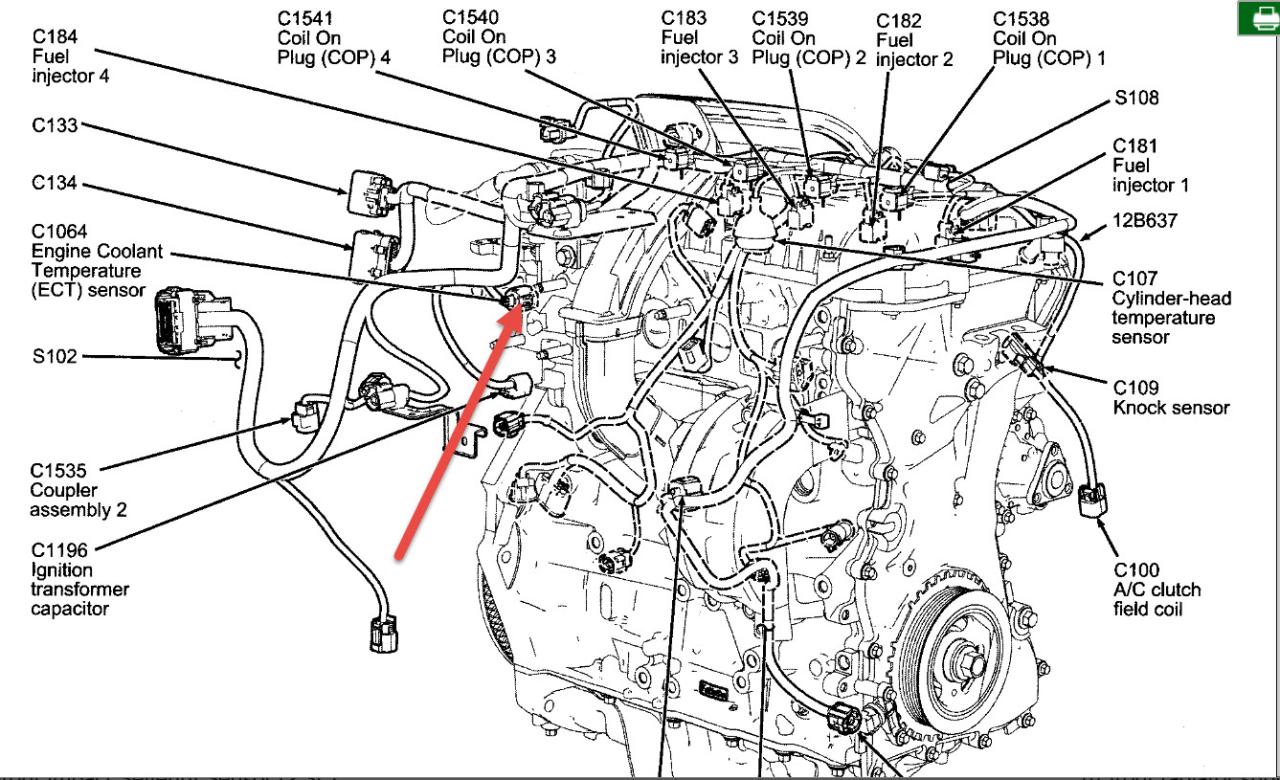
When it comes to the heart of your vehicle, the coolant sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the temperature of the engine’s coolant, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overheating. Understanding its location is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting, so let’s dive into the world of coolant sensor location.
Typically found in various locations depending on the make and model of your vehicle, the coolant sensor is often positioned near the engine block, radiator, or thermostat housing. Its placement is influenced by factors like engine design and cooling system configuration, and locating it requires a keen eye and a step-by-step approach.
Coolant Sensor Purpose and Functionality
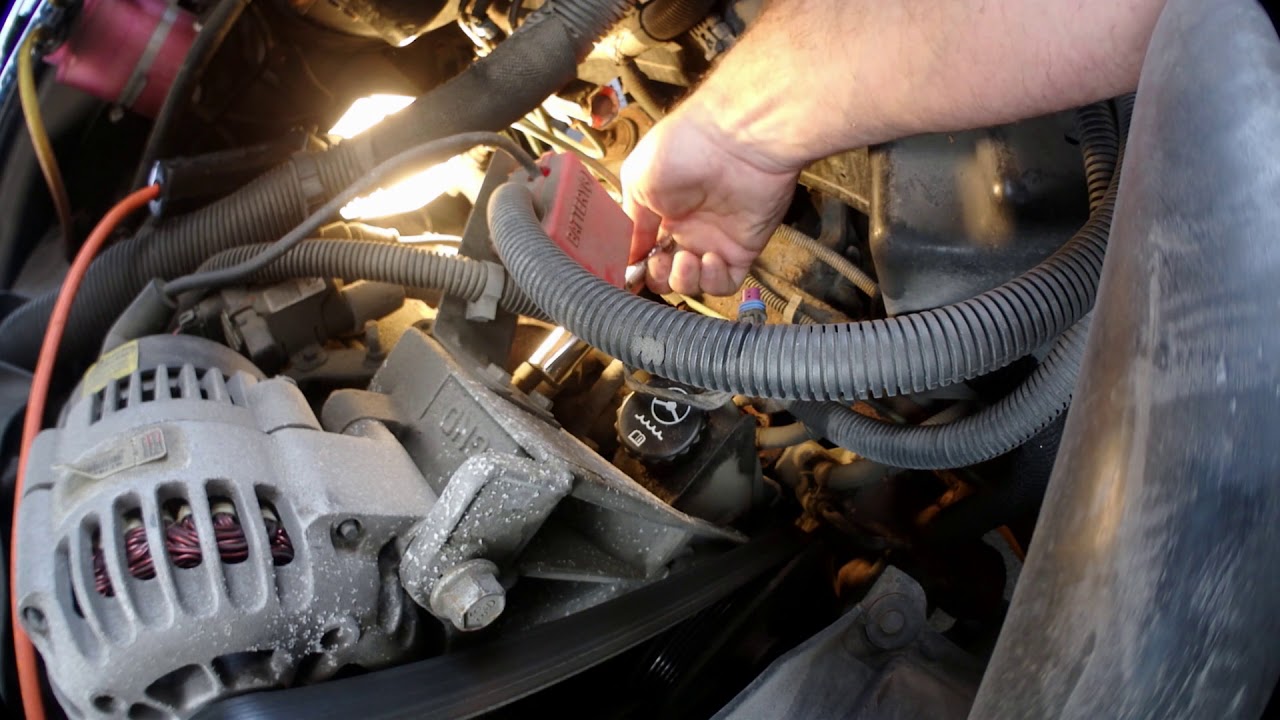

Coolant sensors are crucial components in a vehicle’s engine management system, responsible for monitoring the temperature of the engine coolant. They play a critical role in maintaining optimal engine performance, preventing overheating, and ensuring fuel efficiency.
There are several types of coolant sensors, each employing distinct technologies. One common type is the thermistor, which exhibits a change in electrical resistance with varying temperatures. As the coolant temperature rises, the thermistor’s resistance decreases, allowing more current to flow.
This change in resistance is detected by the engine control unit (ECU), which adjusts the engine’s operating parameters accordingly.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermistors
- Advantages:
- Compact and inexpensive
- Accurate and reliable
- Simple to integrate into engine management systems
- Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to electrical noise and interference
- Limited temperature range
Other types of coolant sensors include thermocouples, which generate a voltage proportional to the temperature difference between the sensor and a reference point, and semiconductor sensors, which utilize semiconductor materials to detect temperature changes.
Coolant Sensor Location Identification
Coolant sensors are typically located in the engine coolant system, near the engine block or radiator. The exact location can vary depending on the vehicle make, model, and engine design.
Factors that influence sensor placement include the engine’s cooling system configuration, the type of coolant sensor used, and the need for easy access for maintenance or replacement.
Locating a Coolant Sensor
To locate a coolant sensor in a specific vehicle, follow these steps:
- Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or online resources for the specific location of the coolant sensor.
- Look for the coolant sensor near the engine block, radiator, or coolant hoses.
- Identify the sensor by its electrical connector or its unique shape and size.
- Disconnect the electrical connector to confirm that it is the coolant sensor.
Coolant Sensor Installation and Replacement
Replacing a coolant sensor is a straightforward task that can be completed in a few simple steps. However, it’s important to take safety precautions and use the correct tools for the job.
Safety Precautions
- Allow the engine to cool completely before starting any work.
- Wear gloves and eye protection to avoid contact with hot coolant.
- Use a torque wrench to tighten the sensor to the specified torque to prevent leaks.
Necessary Tools
- New coolant sensor
- Wrench or socket
- Torque wrench
- Coolant
- Funnel
Using the Correct Sensor
It’s crucial to use the correct coolant sensor for your specific vehicle application. Using an incorrect sensor can lead to inaccurate readings or even damage to the engine.
Coolant Sensor Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting a coolant sensor involves identifying symptoms of a faulty sensor, testing its functionality, and resolving any underlying issues. By understanding the common signs of sensor failure and the methods to test its performance, you can effectively diagnose and fix coolant sensor-related problems.
Symptoms of a Faulty Coolant Sensor
When a coolant sensor malfunctions, it can manifest in several ways. Here are some common symptoms to watch out for:
- Inaccurate temperature readings:The sensor may provide incorrect temperature readings, resulting in the engine running at improper temperatures.
- Engine overheating:A faulty sensor may fail to detect high coolant temperatures, leading to engine overheating.
- Engine stalling:In severe cases, a malfunctioning coolant sensor can cause the engine to stall or run erratically.
- Illuminated check engine light:The vehicle’s check engine light may illuminate due to the sensor’s failure, indicating a problem with the cooling system.
Testing a Coolant Sensor
To determine if the coolant sensor is functioning correctly, you can perform a simple test. Here are the steps involved:
- Disconnect the sensor:Unplug the electrical connector from the coolant sensor.
- Measure resistance:Using a multimeter, measure the resistance between the sensor’s terminals. The resistance should be within the specified range provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Check for continuity:Switch the multimeter to continuity mode and touch the probes to the sensor’s terminals. There should be continuity when the sensor is immersed in coolant.
Troubleshooting Tips
If the coolant sensor test indicates a malfunction, you can follow these troubleshooting tips:
- Check the wiring:Inspect the wiring harness connected to the coolant sensor for any damage or loose connections.
- Clean the sensor:Remove the sensor and clean it with a non-abrasive cleaner to remove any debris or corrosion.
- Replace the sensor:If the wiring and sensor are in good condition, it may be necessary to replace the coolant sensor with a new one.
Coolant Sensor Maintenance and Prevention
Maintaining your coolant system is crucial for preventing sensor failures and extending the lifespan of your vehicle’s engine. Regular coolant flushes remove impurities, such as rust and debris, that can accumulate over time and interfere with the sensor’s ability to accurately measure coolant temperature.
Inspecting and Cleaning a Coolant Sensor
Inspecting and cleaning your coolant sensor periodically can help detect potential issues early on. Locate the sensor in your vehicle’s engine bay and disconnect it from the electrical connector. Use a soft cloth or brush to gently remove any dirt or debris from the sensor’s surface.
Check for any signs of corrosion or damage, and replace the sensor if necessary.
Preventing Coolant Sensor Failures, Coolant sensor location
Preventing coolant sensor failures involves taking proactive measures to maintain the health of your coolant system. Use the manufacturer-recommended coolant type and ensure the coolant level is always at the proper level. Avoid mixing different types of coolant, as this can lead to chemical reactions that can damage the sensor.
Regular coolant flushes and system inspections will help keep your coolant system clean and prevent sensor failures.
Additional Considerations
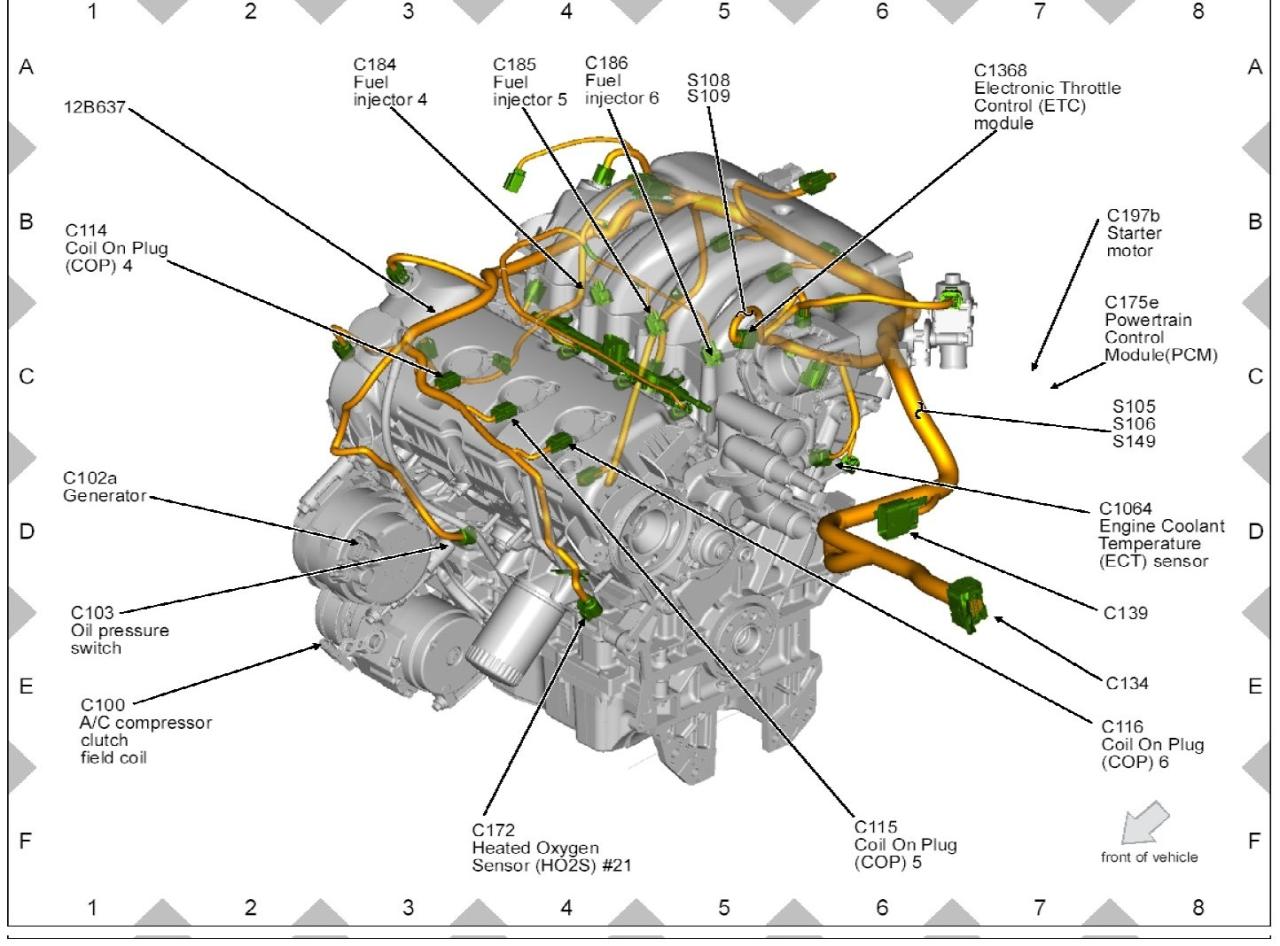
Coolant sensors play a critical role in engine management systems, providing vital data to ensure optimal engine performance. A faulty coolant sensor can have significant consequences for vehicle operation.
The coolant sensor relays temperature information to the engine control unit (ECU), which uses this data to adjust various engine parameters, including fuel injection, ignition timing, and fan speed. Accurate coolant sensor readings are crucial for maintaining proper engine operating temperatures, preventing overheating or undercooling.
Impact of a Faulty Coolant Sensor
A faulty coolant sensor can lead to several issues, including:
- Engine overheating:If the coolant sensor fails to detect high temperatures, the ECU may not activate the cooling fan, leading to engine overheating.
- Engine undercooling:Conversely, a faulty sensor that provides incorrect low temperature readings may prevent the ECU from activating the engine coolant heater, resulting in undercooling.
- Poor fuel economy:Inaccurate coolant temperature readings can affect fuel injection timing, leading to decreased fuel efficiency.
- Reduced engine performance:Engine timing and ignition are adjusted based on coolant temperature. A faulty sensor can disrupt these adjustments, resulting in reduced engine power and responsiveness.
Additional Resources
- YourMechanic: Symptoms of a Bad Coolant Temperature Sensor
- AA1Car: Coolant Temperature Sensor
- AutoZone: Coolant Temperature Sensor Replacement
Final Wrap-Up
From identifying the coolant sensor’s location to troubleshooting any issues, this guide has provided a comprehensive overview of this vital component. Remember, a faulty coolant sensor can impact engine performance, so regular maintenance and prompt replacement are crucial for a healthy and efficient vehicle.
Q&A
Where is the coolant sensor usually located?
The coolant sensor is typically found near the engine block, radiator, or thermostat housing, depending on the vehicle’s make and model.
How can I identify a faulty coolant sensor?
Common symptoms include inaccurate temperature readings, engine overheating, and illuminated warning lights on the dashboard.
Is it difficult to replace a coolant sensor?
Replacing a coolant sensor can vary in difficulty depending on its location and the vehicle’s design. It’s recommended to consult a mechanic if you’re not comfortable performing the task yourself.