Traction control sensor location – Delve into the enigmatic world of traction control sensors, where we embark on an illuminating journey to uncover their strategic placement within the automotive realm. Prepare to unravel the intricacies of these unsung heroes, responsible for maintaining your vehicle’s unwavering grip on the road.
From their pivotal role in ensuring optimal traction to their intricate collaboration with other system components, we delve deep into the fascinating world of traction control sensors, shedding light on their types, functions, and the art of pinpointing their exact whereabouts.
Traction Control System Overview
Traction control is a safety system designed to prevent the wheels of a vehicle from losing grip on the road surface, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery surfaces.
The traction control system monitors the speed of each wheel and compares it to the speed of the engine. If a wheel is spinning faster than the others, it indicates that the wheel is losing traction. The traction control system then applies the brakes to that wheel, slowing it down and restoring traction.
Components of a Traction Control System
The main components of a traction control system include:
- Wheel speed sensors: These sensors measure the speed of each wheel.
- Engine speed sensor: This sensor measures the speed of the engine.
- Traction control module: This module compares the speed of the wheels to the speed of the engine and controls the application of the brakes.
- Brake actuators: These actuators apply the brakes to the wheels when necessary.
Traction Control Sensor Types and Functions
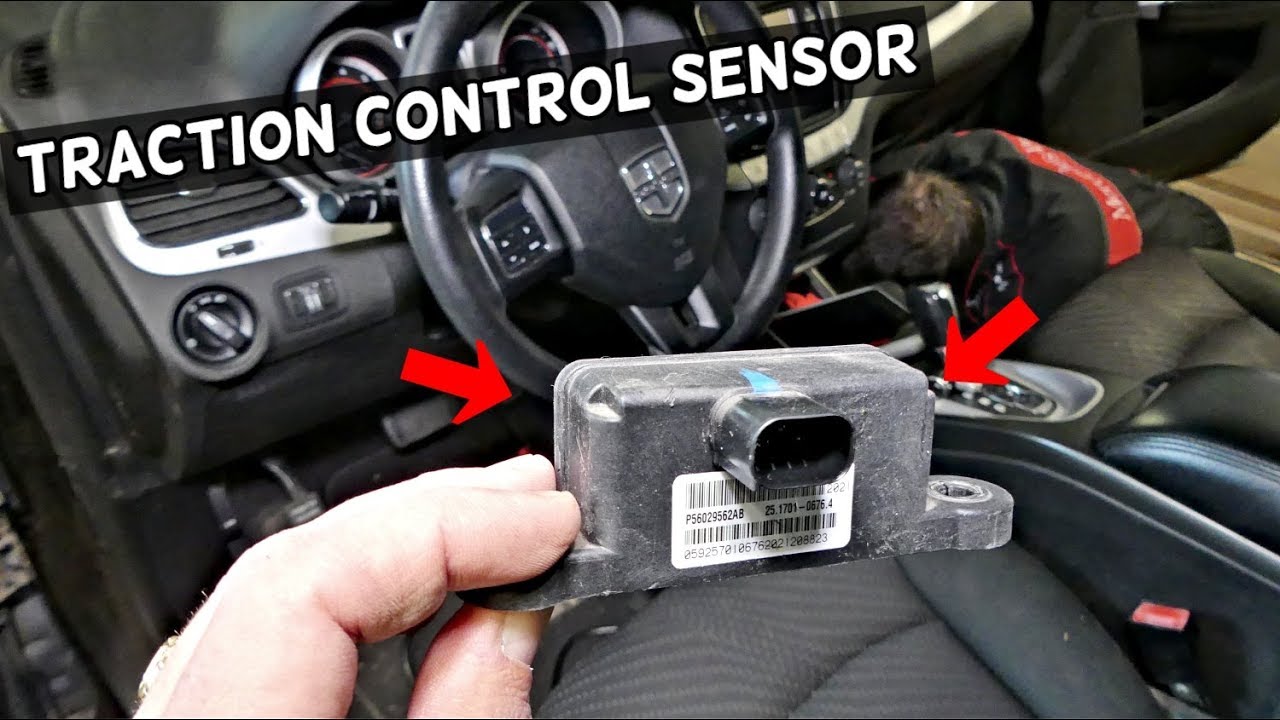

Traction control systems rely on various sensors to monitor vehicle dynamics and detect wheel slip. These sensors provide real-time data that allows the system to intervene and maintain traction.
The most common types of traction control sensors include:
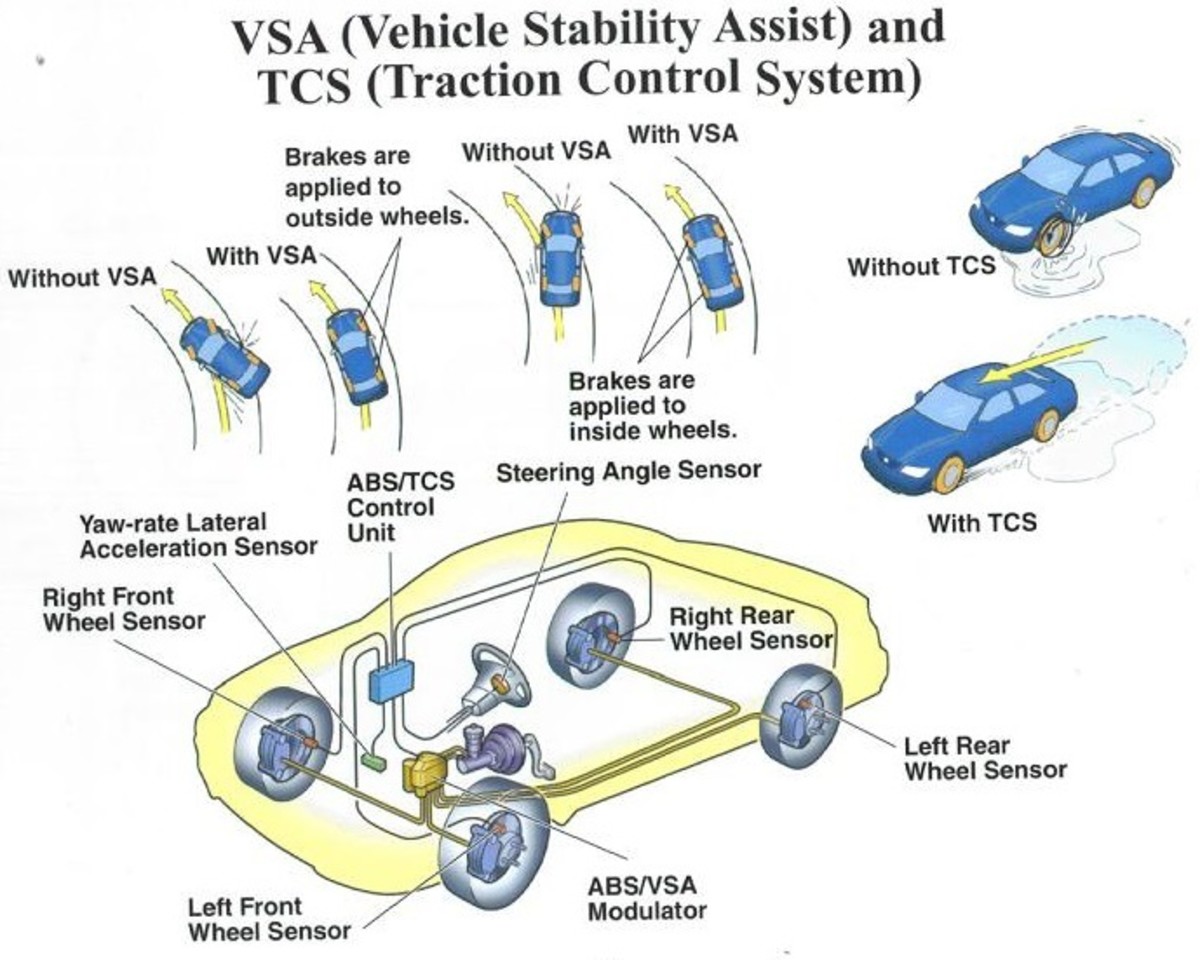
- Wheel Speed Sensors:Measure the rotational speed of each wheel. Differences in wheel speeds indicate wheel slip.
- Yaw Rate Sensors:Detect the vehicle’s rotational motion around its vertical axis. Excessive yaw rate indicates loss of traction.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensors:Measure the vehicle’s lateral acceleration. High lateral acceleration can indicate cornering forces that exceed the tires’ grip limit.
- Steering Angle Sensors:Monitor the steering wheel angle. Unexpected steering angle changes can indicate loss of traction.
- Brake Pressure Sensors:Measure the hydraulic pressure in the brake lines. Changes in brake pressure can indicate wheel slip.
Traction Control Sensor Location
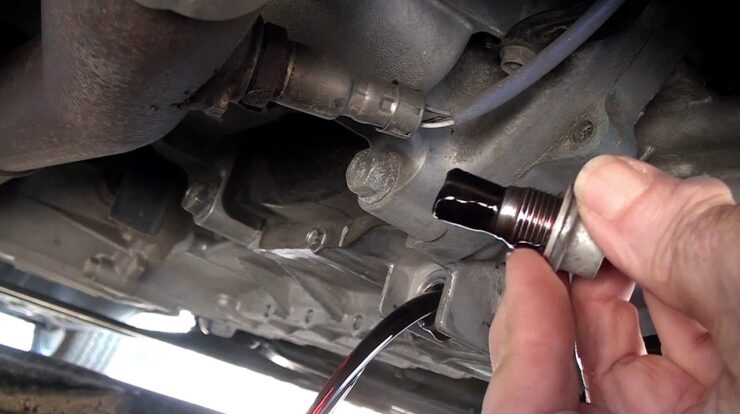
Traction control sensors are typically located near the wheels, where they can detect wheel speed and slippage. On most vehicles, there is one sensor per wheel, mounted either on the wheel hub or the suspension. Some vehicles may have additional sensors, such as a yaw rate sensor or a lateral acceleration sensor, to provide more information to the traction control system.
Specific Placement of Sensors on Different Vehicle Models or Types
The specific placement of traction control sensors can vary depending on the vehicle model or type. On front-wheel drive vehicles, the sensors are typically located on the front wheels. On rear-wheel drive vehicles, the sensors are typically located on the rear wheels.
On all-wheel drive vehicles, the sensors are typically located on all four wheels.The sensors are usually mounted in a location where they are protected from dirt and debris. They are also typically mounted in a way that allows them to easily detect wheel speed and slippage.
Methods for Identifying Traction Control Sensor Location
Identifying the location of traction control sensors is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting. Here are several methods to help you pinpoint their exact position:
Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic tools like OBD-II scanners can provide real-time data on sensor performance. By accessing the vehicle’s computer, you can retrieve trouble codes and sensor readings, often including their specific location.
Repair Manuals
Repair manuals are invaluable resources that contain detailed diagrams and instructions specific to your vehicle model. They provide precise information on the placement of traction control sensors, along with other components.
Visual Inspection
In some cases, traction control sensors may be visible upon visual inspection. Look for small, cylindrical or rectangular devices mounted near the wheels or axles. They may have wires or connectors attached.
Additional Tips
- Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific sensor locations.
- Use a flashlight or headlamp to illuminate the areas around the wheels and axles.
- Follow the wiring harness connected to the sensor to trace its path back to the control module.
Troubleshooting Traction Control Sensor Issues
Traction control sensors play a crucial role in maintaining vehicle stability and preventing wheel spin. When these sensors encounter issues, it can lead to various problems and affect the overall performance of the traction control system. Here are some common symptoms that may indicate a traction control sensor issue:
- Traction control light illuminates on the dashboard
- Vehicle experiences excessive wheel spin or loss of traction
- ABS system may not function properly
- Vehicle may exhibit stability issues during cornering or acceleration
To troubleshoot and diagnose potential traction control sensor problems, follow these steps:
Visual Inspection
Begin by visually inspecting the traction control sensors. Check for any visible damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Clean any dirt or debris that may have accumulated on the sensors.
Electrical Testing
Use a multimeter to test the electrical resistance of the traction control sensors. Compare the readings with the manufacturer’s specifications. If the resistance is significantly different, it may indicate a faulty sensor.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Connect a diagnostic scanner to the vehicle’s OBD-II port. Retrieve any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that may be related to the traction control system. These codes can provide valuable information about the specific sensor or circuit that is causing the issue.
Signal Simulation
Use a scan tool or other diagnostic equipment to simulate a signal from the traction control sensor. Observe the vehicle’s response to determine if the sensor is receiving and processing the signal correctly.
Sensor Replacement
If all other troubleshooting steps fail to resolve the issue, it may be necessary to replace the faulty traction control sensor. Refer to the vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions on how to replace the sensor.
Maintenance and Replacement of Traction Control Sensors: Traction Control Sensor Location
Traction control sensors play a vital role in maintaining vehicle stability and traction. To ensure optimal performance, it’s crucial to adhere to a regular maintenance schedule and replace sensors when necessary. This section will provide insights into the recommended maintenance intervals, safety precautions, and steps involved in replacing traction control sensors.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule
- Inspect traction control sensors visually for any signs of damage or corrosion during regular vehicle maintenance.
- Clean the sensors using a suitable electrical contact cleaner to remove any dirt or debris that may interfere with their operation.
- Check the electrical connections to the sensors to ensure they are secure and free of corrosion.
- Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific maintenance recommendations and intervals.
Replacing Traction Control Sensors, Traction control sensor location
Replacing traction control sensors requires certain safety precautions and specialized tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Safety Precautions:Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before starting any work to avoid electrical hazards.
- Locate the Sensors:Refer to your vehicle’s service manual to identify the location of the traction control sensors.
- Tools Required:Gather the necessary tools, including a socket wrench, screwdriver, and electrical contact cleaner.
- Disconnect the Sensor:Locate the electrical connector attached to the sensor and carefully disconnect it.
- Remove the Sensor:Using the appropriate socket wrench or screwdriver, remove the mounting bolts that hold the sensor in place and gently pull it out.
- Clean the Mounting Surface:Clean the mounting surface where the new sensor will be installed using electrical contact cleaner to remove any dirt or debris.
- Install the New Sensor:Insert the new sensor into the mounting bracket and secure it with the mounting bolts.
- Reconnect the Sensor:Connect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
- Reconnect the Battery:Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Reset the System:Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for any specific steps required to reset the traction control system after replacing a sensor.
Conclusion

In this comprehensive guide, we have navigated the intricate landscape of traction control sensor location, unraveling the mysteries surrounding these enigmatic components. Armed with this newfound knowledge, you are now empowered to diagnose and resolve any traction control sensor issues that may arise, ensuring your vehicle’s unwavering stability and control on any terrain.
General Inquiries
Where can I find the traction control sensor on my vehicle?
The location of the traction control sensor varies depending on the vehicle model and type. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual or consult a qualified mechanic for precise information.
What are the signs of a faulty traction control sensor?
Common symptoms include illuminated warning lights on the dashboard, reduced traction on slippery surfaces, and difficulty maintaining stability during acceleration or cornering.